Communication Cable — Network cable & Telephone cable
Communication cable is supported frequency bandwidth, data transfer rate, and noise immunity.
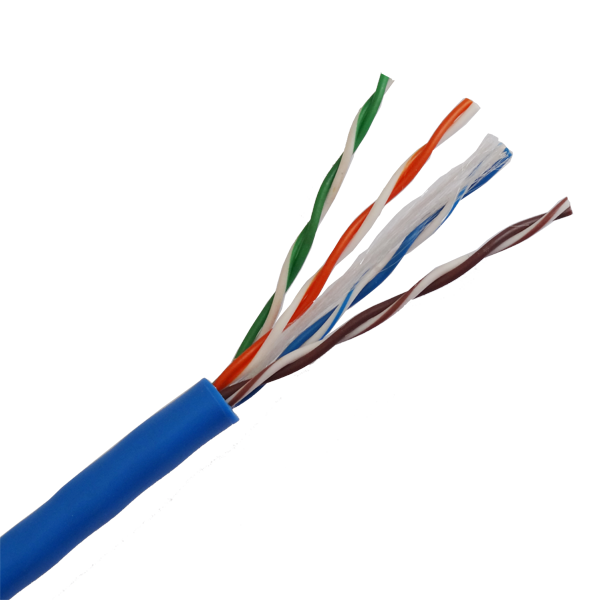
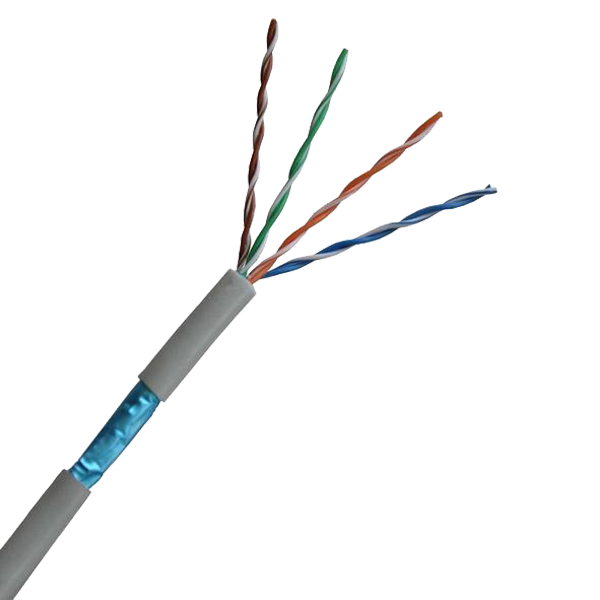
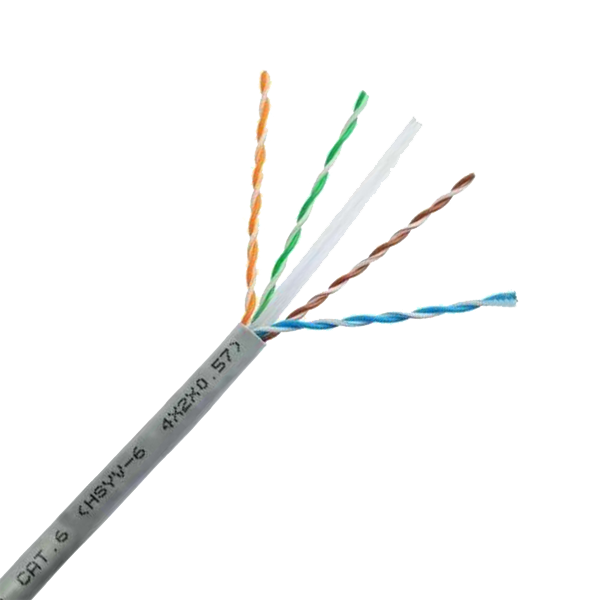
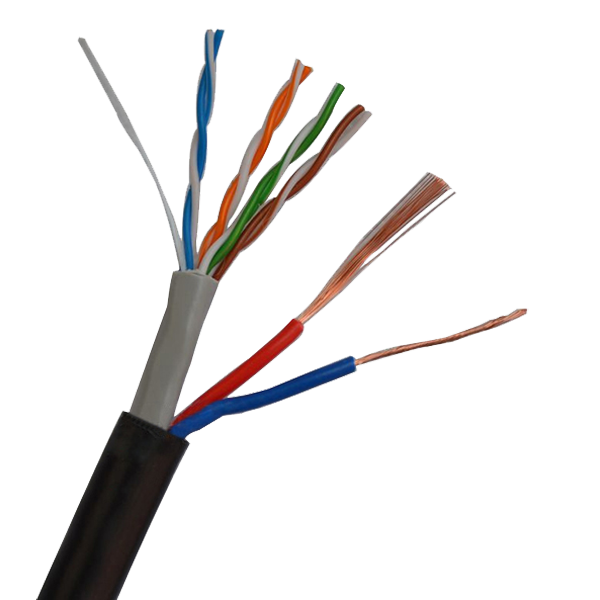




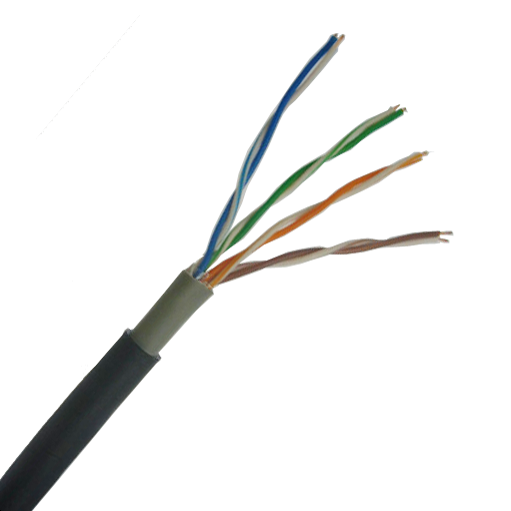
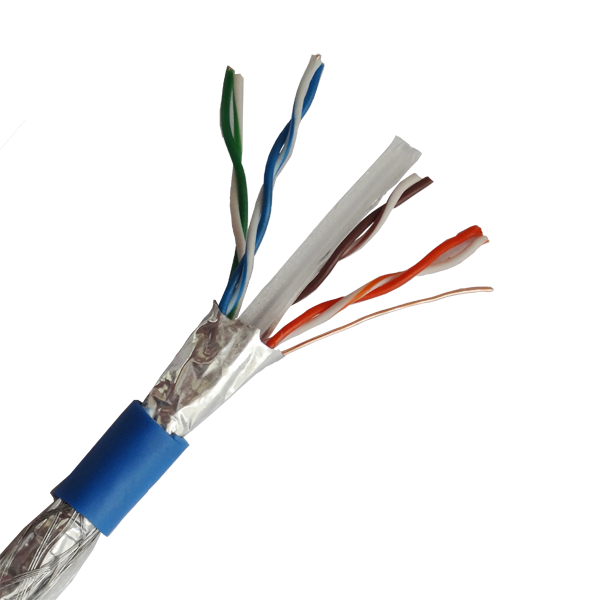
Key Electrical Parameters & Physical Properties
1, Characteristic Impedance: Standard Value: 100 Ω ±15% (i.e., between 85Ω and 115Ω).
2, Attenuation: Must be below a specified limit at standard frequencies and lengths. Lower attenuation allows for longer distances and better signal quality.
3, Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT): A higher NEXT value (a larger negative number) indicates less crosstalk and better performance. E.g., -60 dB is better than -50 dB.
4, Return Loss (RL): A higher RL value (a larger negative number) indicates less reflection and better signal integrity. This is a key indicator of manufacturing precision.
5, Delay Skew: This value must be very small (typically <50 ns/100m). High delay skew can cripple Gigabit+ network performance, as data packets must wait for the slowest pair.
6, Conductor Material:
· Oxygen-Free Copper (OFC): Best choice. Low resistance, high signal efficiency, low attenuation. Often marked “CU”.
· Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA): Inferior performance; higher attenuation over long distances or high frequencies. Not recommended for PoE or Gigabit+ networks.
· Copper-Clad Steel (CCS): Poorest performance, high resistance, suitable only for very short runs.
7, Wire Gauge:
· Unit: AWG (American Wire Gauge). A lower number indicates a thicker wire.
· Common Values:
· Cat 5e/Cat 6: Typically 24 AWG or 23 AWG.
· Cat 6A/Cat 7: Often use thicker 23 AWG or 22 AWG to reduce attenuation.
· Thicker wires have lower resistance, support higher PoE power delivery, and can transmit signals further.
With 25+ years of manufacturing experience, we are your exclusive wire and cable manufacturer
Qunshan Team
